Abstract
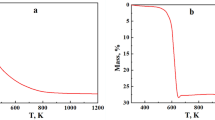
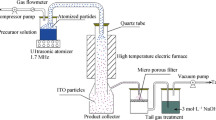
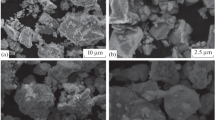
Fluorine-doped tin oxide (FTO) nano-powders were synthesized by a gel combustion method. To analyse the effect of processing factors and their interactions and to achieve an equation for nano-powder particle size in terms of code factors, D-optimal factorial design was used. Stannous chloride penta-hydride, ammonium fluoride and citric acid were used to synthesize the FTO nano-powders. The structure, morphology and composition of the synthesized powders were characterized by X-ray diffraction, field emission scanning electron microscopy and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy, respectively. The results revealed the formation of homogenous FTO nano-powders with an average particle size of 20 nm and equiaxed morphology in the concentration of precursor 0.2, citric acid to precursor molar ratio of 1 and pH of 0.5. The average particle size increased as the concentration of the precursor, citric acid to precursor molar ratio and pH increased from 0.2 to 1, 1 to 3 and 0.5 to 3, respectively. Citric acid to precursor molar ratio, concentration of the precursor and the pH had the most significant effect on the synthesis of the FTO nano-powders, respectively.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hara K, Arakawa H, Luque A and Hegedus S 2003 A Luque handbook of photovoltaic science and engineering (NY: John Wiley & Sons Ltd) p 663
Fortunato E, Ginley D, Hosono H and Paine D C 2007 MRS Bull. 32 242
Li B, Huang L, Zhou M and Wu B 2014 Ceram. Int. 40 1627
Kawashima T, Ezure T, Okada K, Matsui H, Goto K and Tanab N 2004 J. Photochem. Photobiol. 164 199
Tatar D, Turgut G and Duzgun B 2013 Rom. J. Phys. 58 143
Bhardwaj A, Gupta B K, Raza A, Sharma A K and Agnihotri O P 1981 Sol. Energy Mat. Sol. C 5 39
Naje A N, Norry A S and Suhail A M 2013 Int. J. Innov. Res. Sci. Eng. Technol. 42 7068
Farrukh M A, Heng B and Adnan R 2010 Turk. J. Chem. 34 537
Han C H, Jousseaume B, Rascle M C, Toupance T, Cacher H and Vivier V 2004 J. Fluor. Chem. 125 1247
Razeghizadeh A R, Rafee V and Zalaghi L 2015 Mesoscale and nanoscale physics (cond-mat.mes-hall) 142 arXiv:1502.00219
Senthilkumar V, Vickraman P and Ravikumar R 2010 J. Sol. Gel. Sci. Technol. 53 316
Adnan R, Razana N, Rahman I A and Farrukh M A 2010 J. Chin. Chem. Soc. 57 222
Han C H, Han S D, Gwak J and Khatkar S P 2007 Mater. Lett. 61 1701
Yue Z, Li L, Zhou J, Zhang H and Gui Z 1999 Mater. Sci. Eng. B 64 68
Ahmed W and Jackson M J 2009 Emerging nanotechnologies for manufacturing (UK: Elseiver Science and Technology Books)
Telford J K 2007 A brief introduction to design of experiments (Washington: Johns Hopkins APL Technical Digest) p 224
Antony J 2003 Design of experiments for engineers and scientists (Amsterdam: Elsevier Science & Technology Books)
Leiviskä K 2013 Introduction to experiment design (University of Oulu) p 31
Kehoe S, Ardhaoui M and Stokes J 2011 J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 20 1423
Askari-Paykani M, Shayan M and Shamanian M 2014 J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 21 252
Software Help Design-Expert Software, Version 7.1 2007 User’s guide, technical manual (Minneapolis, MN: Stat-Ease Inc.)
Nekouei R K, Rashchi F and Amadeh A 2013 Powder Technol. 237 165
Sikhwivhilu L M, Pillai S K and Hillie T K 2011 J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 11 4988
Li Z, Shen W, Zhang X, Fang L and Zu X 2008 Colloids Surf. A: Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 17 327
Bruneaux J, Cachet H, Froment M, Levart M, and Vedel J 1989 J. Microsc. Spectrosc. Electron. 14 1
Riahi-Noori N, Sarraf-Mamoory R, Alizadeh P and Mehdikhani A 2008 J. Ceram. Process. Res. 9 246
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Malek, S., Baghshahi, S., Sarraf-Mamoory, R. et al. Gel combustion synthesis of fluorine-doped tin oxide and its characteristics: applying D-optimal factorial design of experiment. Bull Mater Sci 42, 109 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12034-019-1769-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12034-019-1769-5